Polymer film (thermoplastic materials)
A wide selection of polymer films with a wide range of properties which can be transformed into a variety of shapes and sizes. Compared to other materials, plastic is very flexible, durable and cost-effective. This is the main reason why this material is among the most frequently used in the production of flexible packaging.
The following polymer films are most often used for the production of flexible packaging in our company:
- LDPE (polyethylene) Extremely flexible and durable material, resistant to low temperatures, with high impermeability levels. It can be welded by itself, without the additional use of coatings and adhesives. LDPE is one of the most commonly used welding materials for the production of flexible packaging.
- PET (polyethylene terephthalate) This film is extremely transparent, relatively non-reactive (in contact with other substances), provides a high level of air tightness (oxygen), has excellent tensile strength and is resistant to high temperatures. It is often used as a surface film in lamination, which is necessary to protect food from oxidation and loss of aroma (e.g. coffee packaging or pouches for various foods). Mono PET is a material used for lid films for fresh or frozen ready-made dishes.
- BOPP (polypropylene) Polypropylene film is highly resistant to moisture and grease. Particularly because of its low absorption, moisture permeability and high chemical resistance, this material is used to produce high-quality medical packaging.
- BOPA (polyamide) Polyamide film is distinguished by a high degree of transparency. It is extremely durable and has a very high resistance to penetration (it is difficult to pierce). In flexible packaging, it serves as an effective barrier to oxygen, chemicals and aromas.
(Kraft) paper
(Kraft) paper has high tensile strength, elasticity and a relatively good tearing resistance. It offers a certain measure of support and strength to the product. It is used for packaging products, such as multi-layered paper bags and bags (for cement, food, chemicals, flour, etc.) as well as bags for bakery products and other consumer packaged goods.
Aluminium film
Metallised aluminium film is the best choice of packaging material to ensure a 100% barrier for all types of gases, liquids (moisture) or light. It deflects infra-red rays in an excellent way. It is very rarely used independently, as it breaks when folded. It provides a bad barrier for aromas when used independently, therefore it is used in multi-layer structures along with polymer films or paper, which enables a significantly improved flexibility. It has numerous applications: caps for dairy products e.g. yoghurt, flavoured drinks, cosmetics, foodstuffs, confectionery and ready-made dishes, soups, sauces, canned and liquid food, pharmaceuticals.
Cellulose and biodegradable materials
Effectively prevent oxygen, grease and oil permeability, but represent a weak barrier for liquids or moisture (without coatings or laminations). Cellulose and biodegradable films can easily be degraded and composted. The use of such materials has increased significantly in the recent years, especially in the food industry, especially for packaging bakery products, confectionery, fast food products and various snacks.
It is of great importance to select the right material of flexible packaging when choosing a product design.
Composition of packaging material – single-layer and multi-layer
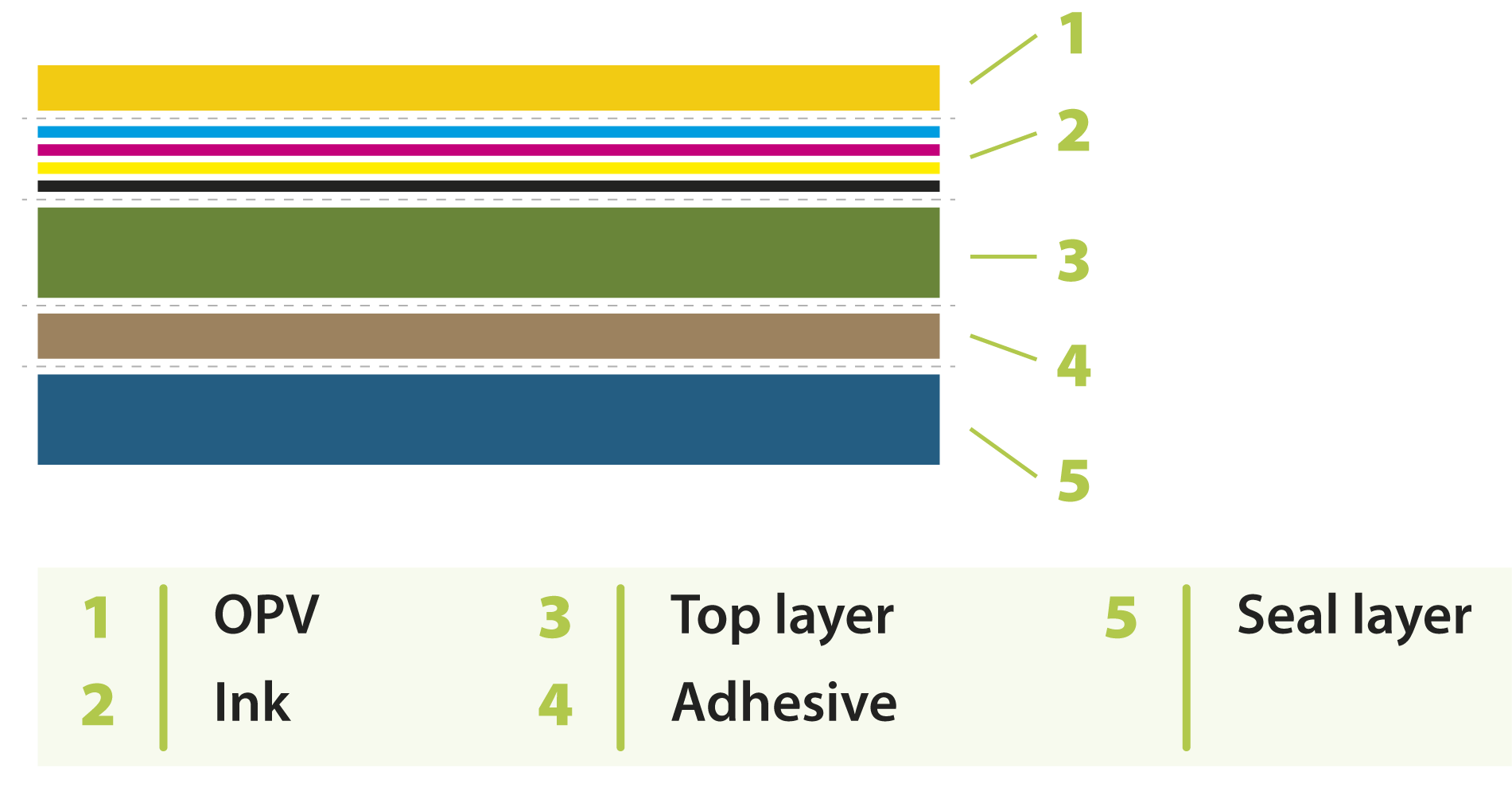
Packaging material can be single-layer when it is made of only one type or layer of material (substrate), or multi-layer when it consists of several layers (of the same or different) materials. The latter is used when several different parameters and barriers need to be taken into account to ensure product protection. Each layer in the multi-layer packaging structure has a specific protective function, such as: preventing contamination, preserving freshness, protection against mechanical damage (bumps, scratches, scrapes), ensuring tensile strength and tightness of the packaging.
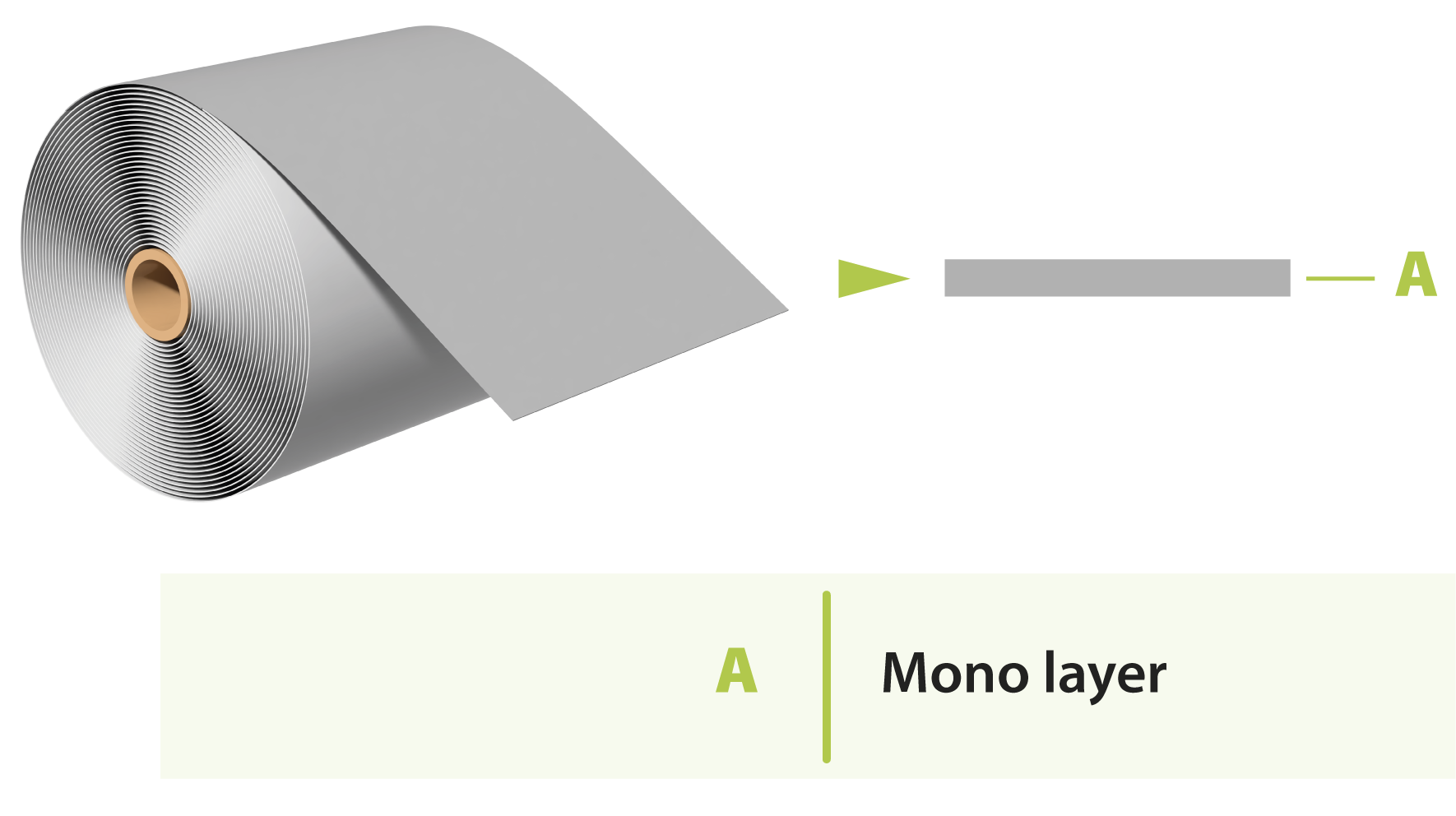
Single-layer material
Double-layer material
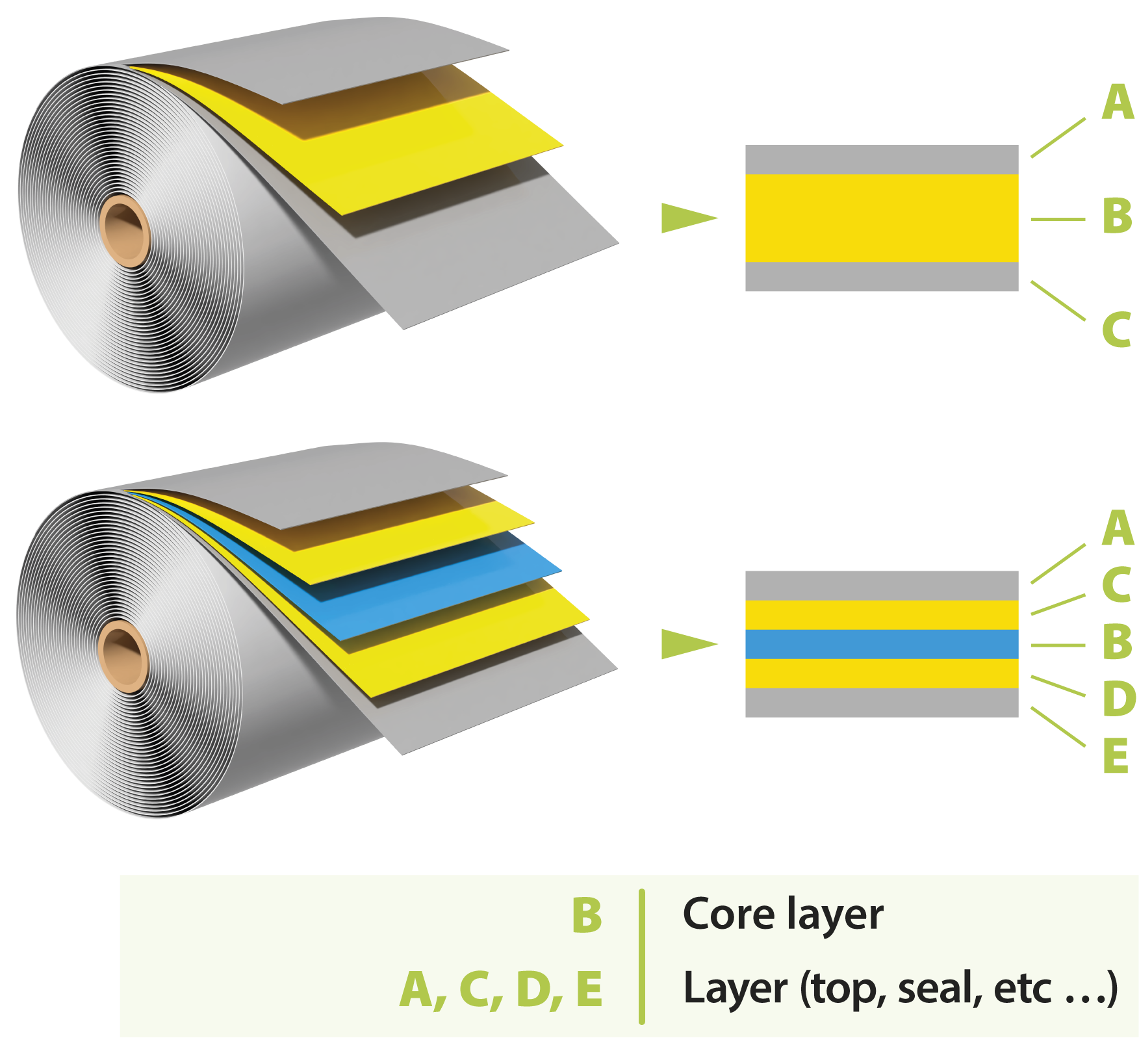
Composition of multi-layer materials
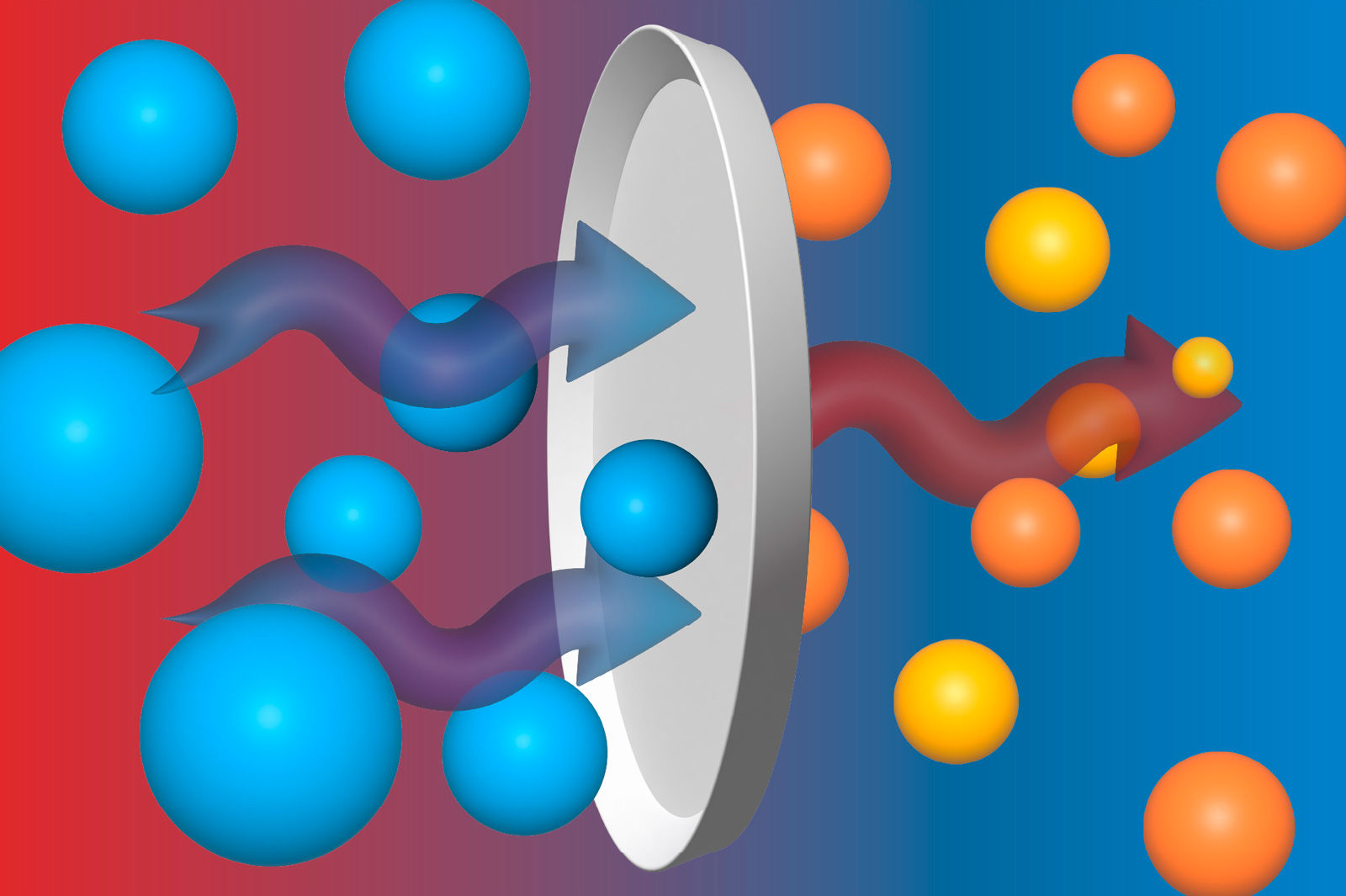
Material permeability – barrier properties
Flexible packaging, made of multi-layer materials (using the lamination process), can provide a high range of barrier properties, the basic function of which is to protect the product (most often food) from the penetration (or leakage) of substances (oxygen, carbon dioxide and aromas) into or out of the packaging.